This blog explores effective strategies for on-demand app monetization in 2024. We’ll cover the freemium model, in-app purchases, tiered subscriptions, and additional revenue streams like commissions and data insights. Remember, user experience reigns supreme – prioritize it to ensure your app flourishes in the on-demand economy.
In this blog, we’re going to discuss📝
The on-demand app revolution has become an undeniable force, fundamentally altering how we access services and goods. From the comfort of our homes, we can now summon groceries, laundry services, fitness instructors, and even pet care – all with a few taps on our smartphone. But for the enterprising minds behind these on-demand apps, a crucial question remains: how can they translate this tsunami of user interaction into a sustainable business model?
This blog post is a roadmap to success. We’ll delve into the top monetization strategies that will keep your on-demand app thriving in the ever-evolving landscape of 2024.
Top Monetization Strategies for On-Demand Apps in 2024
The cost efficient on-demand app revolution has transformed the way we live, offering instant access to everything from groceries and rides to fitness classes and pet care. But how do these apps, constantly striving to provide seamless convenience, translate that into a sustainable business model? Buckle up, because we’re diving deep into the top monetization strategies for on-demand apps in 2024!
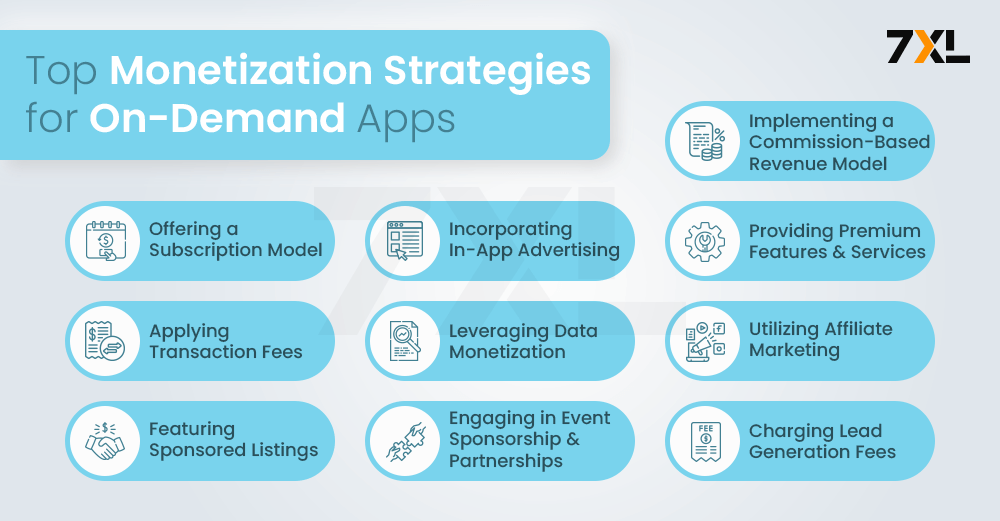
1. Commission-Based Revenue Model
Overview: The commission-based model is a fundamental monetization strategy for on-demand apps. It involves charging service providers a percentage of each transaction facilitated through the app.
How It Works:
- Transaction Fee: The app takes a commission from each transaction, typically ranging from 10% to 30% of the total service or product cost.
- Variable Rates: Commission rates can vary based on factors such as service type, provider rating, or transaction volume.
Advantages:
- Scalable Income: As the number of transactions increases, so does the revenue, making it a scalable model.
- Low Entry Barrier: Encourages service providers to join the platform with minimal upfront costs.
Disadvantages:
- Provider Resistance: High commission rates might deter providers, especially if they feel it significantly reduces their profit margins.
- Pricing Impact: Providers may increase prices to cover commission costs, potentially affecting customer satisfaction.
Examples:
- Uber: Charges drivers a commission for each ride completed through the app, with rates typically around 25%.
2. Subscription Model
Overview: The subscription model provides users and service providers with access to exclusive features or benefits for a recurring fee. This model generates a steady revenue stream and fosters long-term engagement.
How It Works:
- User Subscriptions: Users can subscribe to monthly or yearly plans that offer benefits like discounts, priority service, or premium features.
- Provider Subscriptions: Service providers can pay for access to advanced features such as enhanced visibility, analytics, and lead generation tools.
Advantages:
- Predictable Revenue: Regular subscription payments ensure consistent income, aiding in financial stability and planning.
- Increased Retention: Subscribers are more likely to remain engaged with the app to maximize their subscription benefits.
Disadvantages:
- Conversion Challenge: Convincing free users to upgrade to paid subscriptions can be difficult, requiring compelling value propositions.
- User Churn: Retaining long-term subscribers can be challenging in a competitive market.
Examples:
- Spotify: Offers a subscription service that provides ad-free music streaming, offline listening, and exclusive content.
3. In-App Advertising
Overview: In-app advertising is a significant revenue generator for on-demand apps. This model leverages the app’s user base to display ads from third-party businesses, creating an additional income stream.
How It Works:
- Ad Placement: Ads are strategically placed within the app, including banners, pop-ups, and video ads. Advertisers pay for these placements based on impressions, clicks, or conversions.
- Targeted Ads: Utilize user data to display relevant ads that match their interests & needs, increasing ad effectiveness and engagement.
Advantages:
- Additional Revenue: In-app ads provide a substantial income source without directly charging users for access.
- Brand Partnerships: Advertising creates opportunities for collaborations with brands that align with the app’s services and user base.
Disadvantages:
- User Experience Impact: Excessive or intrusive ads can disrupt the user experience and lead to dissatisfaction.
- Ad Relevance: Ensuring ads are relevant and non-disruptive is crucial to maintain user engagement and trust.
Examples:
- YouTube: Generates significant revenue from in-app ads, including banners, video ads, and sponsored content.
4. Premium Features and Services
Overview: Offering premium features and services provides a way to monetize additional functionalities that enhance the user experience. Users pay for access to these features, which can offer convenience, advanced capabilities, or exclusive content.
How It Works:
- User Enhancements: Users can purchase features like priority service, advanced search filters, or exclusive access to premium content.
- Provider Tools: Service providers can pay for advanced tools such as analytics, marketing resources, or enhanced visibility.
Advantages:
- Increased Revenue: Premium features provide an additional revenue stream by catering to users willing to pay for enhanced services.
- User Satisfaction: High-quality, convenient features can improve user satisfaction and retention.
Disadvantages:
- Cost Sensitivity: Some users may be reluctant to pay for features they believe should be included for free.
- Feature Management: Managing and maintaining a variety of premium features can be resource-intensive.
Examples:
- LinkedIn Premium: Offers advanced job search tools, insights into who viewed your profile, and the ability to message users outside your network.
5. Transaction Fees
Overview: Charging transaction fees is a straightforward way to generate revenue from each payment processed through the app. This model applies to various types of transactions, including service payments, product purchases, or in-app purchases.
How It Works:
- Processing Fees: Charge a fee for processing payments made through the app, which may represent a percentage of the transaction or a set value.
- Service Fees: Apply additional service fees for premium services or features, such as express delivery or priority service.
Advantages:
- Consistent Revenue: Generates income with each transaction, providing a reliable revenue stream.
- User Flexibility: Allows users to pay for additional services as needed, enhancing their experience.
Disadvantages:
- User Resistance: Users may be sensitive to extra fees, potentially affecting their willingness to use the app.
- Cost Management: Balancing transaction fees to ensure profitability while remaining attractive to users can be challenging.
Examples:
- PayPal: Charges transaction fees for payments processed through its platform, including a percentage of the transaction amount and a fixed fee.
6. Data Monetization
Overview: Data monetization involves leveraging user data to generate revenue. On-demand apps collect vast amounts of data that can be valuable for market research, product development, and targeted marketing.
How It Works:
- Data Analysis: Collect & analyze user data to gain insights into behavior, preferences, and trends.
- Data Sales: Sell aggregated and anonymized data to third parties for market research and analysis.
Advantages:
- High Value: User data is a valuable asset for businesses looking to understand consumer behavior & market trends.
- Non-Disruptive: Generates revenue without directly impacting the user experience, making it an attractive option for additional income.
Disadvantages:
- Privacy Concerns: Requires strict adherence to privacy regulations and ethical guidelines to avoid legal issues and maintain user trust.
- User Trust: Maintaining user trust is critical, as data monetization practices can raise concerns about data privacy and security.
Examples:
- Facebook: Monetizes user data by selling targeted advertising based on user interests and behavior, generating significant revenue.
7. Affiliate Marketing
Overview: Affiliate marketing involves endorsing products or services from partner companies within the app and earning a commission on sales generated through referrals. This model provides an additional revenue stream and enhances the app’s value proposition.
How It Works:
- Product Promotions: The app features products or services from affiliate partners, and users can purchase these items through referral links.
- Commission Earnings: The app earns a commission for each sale made through its referral links, providing a steady income stream.
Advantages:
- Revenue Sharing: Generates additional income without significant investment in new content or features.
- Extended Offerings: Enhances the app’s value by promoting relevant products and services that align with user needs.
Disadvantages:
- Quality Control: Ensuring that affiliate products meet the app’s quality standards is crucial to maintain user trust and satisfaction.
- Revenue Split: The revenue is shared with partners, potentially reducing overall profitability.
Examples:
- Amazon Associates: Offers commissions to affiliates who promote and sell products from Amazon through their platforms.
8. Sponsored Listings
Overview: Sponsored listings involve charging service providers or businesses for premium placement within the app. This model increases visibility for sponsors, leading to higher engagement and revenue.
How It Works:
- Priority Placement: Providers pay to have their listings featured prominently in search results or on the app’s homepage, increasing their visibility and customer inquiries.
- Sponsored Content: Businesses can sponsor specific categories or services, offering them prominent placement and enhanced visibility within the app.
Advantages:
- Increased Visibility: Provides a competitive advantage for providers, helping them attract more customers & grow their business.
- Steady Income: Generates a consistent revenue stream from providers willing to invest in premium placements to boost their visibility.
Disadvantages:
- Fairness Concerns: Overemphasis on paid placements might lead to perceptions of unfair advantage and affect the app’s credibility among users.
- Balance Needed: The app must balance paid and organic listings to ensure a fair and trustworthy user experience.
Examples:
- Google Ads: Charges businesses for sponsored listings that appear at the top of search results, increasing their visibility to potential customers.
9. Event Sponsorship and Partnerships
Overview: Event sponsorships and partnerships involve collaborating with businesses or organizations to sponsor events, activities, or content within the app. This model generates revenue while enhancing user engagement and brand visibility.
How It Works:
- Event Sponsorships: Companies pay to sponsor events or activities within the app, such as webinars, virtual meetups, or exclusive content.
- Partnership Deals: Collaborate with businesses to offer co-branded services or promotions that provide mutual benefits and increased visibility.
Advantages:
- Additional Revenue: Provides a lucrative income source from sponsorships and partnerships.
- Brand Engagement: Creates opportunities for user engagement through sponsored events and activities, enhancing the app’s value proposition.
Disadvantages:
- Resource Intensive: Organizing and managing events and partnerships requires significant resources and coordination.
Examples:
- Eventbrite: Generates revenue through event sponsorships and partnerships, offering businesses access to its large user base for event promotions.
10. Lead Generation Fees
Overview
- Description: Charge service providers for each lead or potential customer generated through the app, regardless of whether the lead converts into a sale.
How It Works
- Lead Purchase: Service providers pay a fee for each lead, such as a user inquiry or booking request.
- Fee Structure: Set fees based on lead quality and potential value, with higher fees for more valuable leads.
Benefits
- Immediate Revenue: Provides upfront revenue from each lead, creating a steady income stream.
- Value for Providers: Encourages service providers to engage with high-quality leads, increasing conversion rates.
Example
- Home Advisor charges service providers for each lead generated through its platform, providing a reliable revenue source.

Want custom On-Demand App Solutions?
At 7xcel, our on-demand app solutions deliver customized, end-to-end excellence to meet all your specific needs efficiently.
Challenges in Monetizing On-Demand Apps
Monetizing comes with significant challenges in on-demand app development, including market saturation, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining consistent service quality. Balancing revenue goals with user satisfaction while navigating these obstacles is crucial for long-term success in the competitive app landscape:
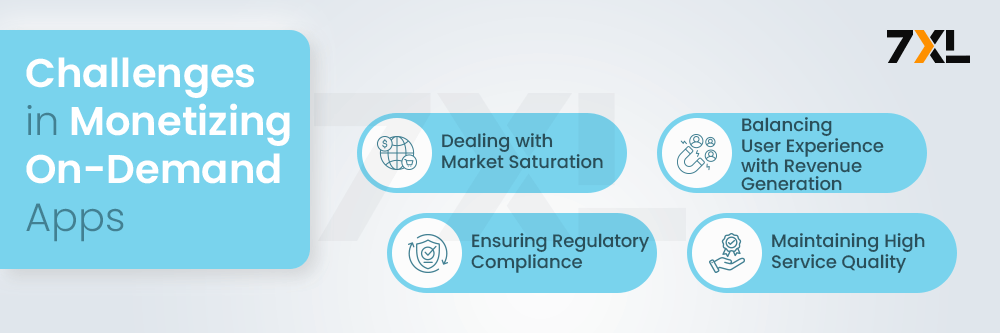
1. Market Saturation
- Overview: The on-demand app market is highly competitive, making it difficult to differentiate and attract users.
- Solution: Focus on unique features and superior service quality to stand out from competitors.
2. Balancing User Experience and Revenue
- Overview: It’s crucial to find a balance between generating revenue & maintaining a positive user experience.
- Solution: Ensure monetization features are non-intrusive and add value to the user.
3. Regulatory Compliance
- Overview: On-demand apps must comply with various regulations, including data privacy and financial transactions.
- Solution: Implement robust compliance measures and stay updated with regulatory changes.
4. Maintaining Service Quality
- Overview: Ensuring consistent service quality across providers can be challenging.
- Solution: Establish rigorous vetting and review processes for service providers.
Best Practices for Monetizing On-Demand Apps
Implementing best practices for monetizing on-demand apps involves understanding user needs, prioritizing seamless monetization integration, and diversifying revenue streams. Adapting to regulatory changes and continuously innovating to enhance user experience are key to achieving sustainable revenue and growth:
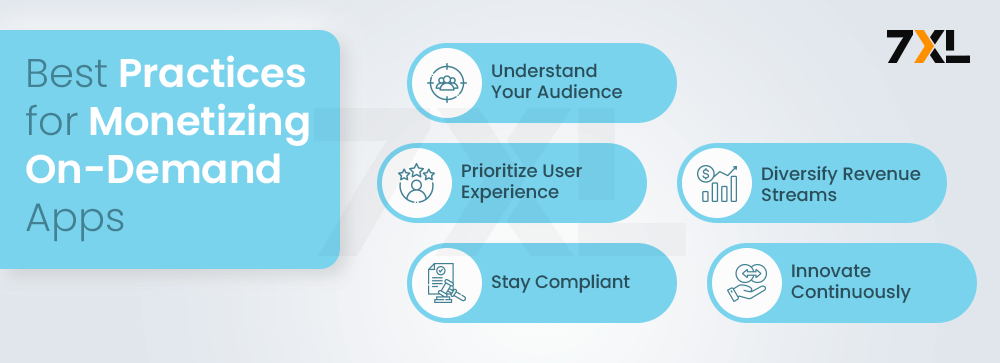
1. Understand Your Audience
- Conduct extensive market research to understand user needs and preferences.
- Tailor monetization strategies to align with user behaviour and expectations.
2. Prioritize User Experience
- Integrate monetization features in a way that enhances rather than disrupts user experience.
- Provide clear value propositions for paid features and services.
3. Diversify Revenue Streams
- Implement multiple monetization models to create a balanced and sustainable income.
- Explore new opportunities for revenue generation, such as partnerships and data insights.
4. Stay Compliant
- Regularly review and update compliance practices to adhere to regulations.
- Maintain transparency with users regarding data usage and monetization practices.
5. Innovate Continuously
- Keep up with industry trends and continuously improve the app with new features.
- Use user feedback to refine and enhance monetization strategies.
Conclusion
Monetizing an on-demand app requires a strategic approach that balances revenue generation with user satisfaction and engagement. By leveraging a combination of commission fees, subscriptions, in-app purchases, advertising, and innovative partnerships, on-demand apps can create sustainable and diverse revenue streams.
As the market evolves, staying adaptable and focusing on user needs will be key to achieving long-term success. Implementing these monetization strategies will help you unlock the full revenue potential of your on-demand app & ensure its continued growth and competitiveness in a dynamic market.