Quick Summary:
Exploring monetization strategies for Uber-like apps involves leveraging diverse approaches to generate sustainable revenue. This blog delves into various tactics that enhance user value and support long-term growth in the competitive on-demand market. By implementing these strategies, app developers can ensure profitability and maintain a strong income stream in this fast-paced industry.
In this blog, we’re going to discuss📝
Uber has revolutionized on-demand transportation, inspiring many to develop similar apps. However, creating a successful app isn’t enough; smart revenue models are crucial for long-term success. This blog explores various monetization strategies for Uber-like apps, detailing their advantages, challenges, and best practices. Whether you’re a new entrepreneur or an industry veteran, this guide offers valuable insights to help you maximize the revenue potential of your Uber-like app.
Understanding the Uber-like App Ecosystem
Before we dive into the revenue models, it’s essential to understand the key components and stakeholders that make up the Uber-like app ecosystem. At its core, an Uber-like app connects three primary groups:
- Riders: The end-users who request and utilize the transportation services provided through the app.
- Drivers: The independent service providers who offer their vehicles and driving services to fulfill ride requests.
- The Platform: The technology-driven company that owns and operates the Uber-like app, facilitating the interactions between riders and drivers.
The success of an Uber-like app hinges on the ability to create a seamless & efficient experience for both riders and drivers, while also generating sustainable revenue for the platform itself. This delicate balance is the foundation upon which effective monetization strategies must be built.
Monetization Stats for App-like Uber
- 71% of users are willing to watch the ads in exchange for free app access.
- On an average there are 80 apps that are installed on the smartphone [Idea Usher]
- Consumers tend to spend 3.8 trillion hours on the mobile apps in 2022
- The retention rate for Android apps is 22.6% one day from the download, 6.5% seven days from download, and 2.6% 30 days after download
- The retention rate for iOS apps is 25.6% a day from download, and 4.3% 30 days after download.
Revenue Models for Uber-like Apps
Uber-like apps have pioneered a range of innovative revenue models, each with its own unique advantages and challenges. Partnering with a specialized Taxi Booking App Development Company can help in identifying and implementing the most effective monetization strategies tailored to the specific needs of the market.
Their expertise can assist in integrating features such as surge pricing, subscription models, and partnerships with local businesses, maximizing revenue potential while ensuring a smooth user experience. Let’s explore the most prominent monetization strategies:
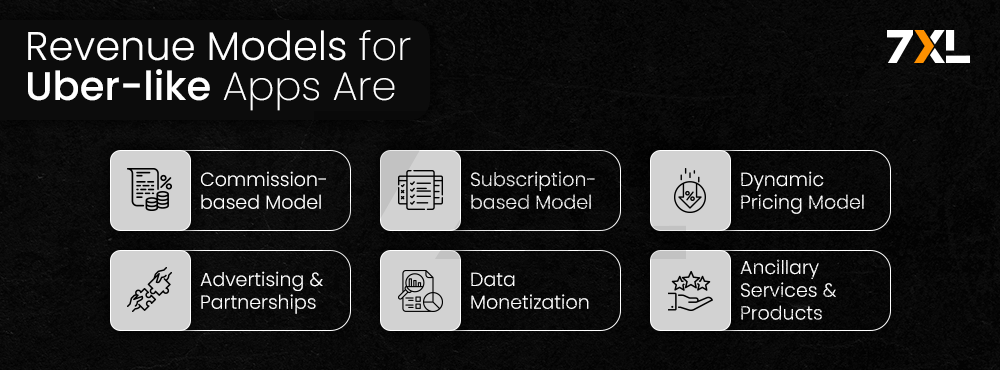
1. Commission-based Model
The commission-based model is the cornerstone of Uber’s revenue generation, and it has become a widely adopted approach in the on-demand transportation industry. In this model, the platform charges a percentage-based commission on each ride completed through the app.
Advantages:
- Scalable Revenue: As the number of rides increases, the platform’s revenue scales proportionally, making it a highly scalable model.
- Alignment of Interests: The commission-based model aligns the interests of the platform, riders, and drivers, as the platform’s success is directly tied to the growth and utilization of the service.
- Minimal Upfront Costs: The platform does not need to invest in a fleet of vehicles or employ drivers, as it relies on the independent service providers to supply the transportation services.
Challenges:
- Potential Driver Dissatisfaction: Drivers may feel that the commission charged by the platform is too high, leading to potential conflicts and driver turnover.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulatory bodies may scrutinize the commission-based model, particularly in terms of labor laws and the classification of drivers as independent contractors.
- Competitive Pressure: As the market becomes more saturated, platforms may need to adjust their commission rates to remain competitive, which can impact overall profitability.
2. Subscription-based Model
For access to the platform’s transportation services, users in the subscription-based model pay a regular price, usually once a month or once a year. This model can be offered as a standalone option or in conjunction with the commission-based approach.
Advantages:
- Predictable Revenue Stream: Subscription-based revenue provides a more predictable and stable income stream for the platform, allowing for better financial planning and forecasting.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Subscribers are more likely to remain loyal to the platform, as they have a vested interest in maximizing the value of their subscription.
- Potential for Upselling: The platform can offer additional premium features or services to subscribers, creating opportunities for further revenue generation.
Challenges:
- Acquiring and Retaining Subscribers: Convincing riders to commit to a subscription-based model can be challenging, especially in a competitive market.
- Balancing Subscription Fees: The platform must strike the right balance between subscription fees and the perceived value of the service to ensure affordability and profitability.
- Potential Cannibalization of Commission-based Revenue: Introducing a subscription model may lead to a decrease in commission-based revenue if riders opt for the subscription option.
3. Dynamic Pricing Model
The dynamic pricing model, also known as surge pricing, is a strategy where the platform adjusts ride prices based on real-time supply and demand factors, such as peak hours, weather conditions, and special events.
Advantages:
- Demand Management: Dynamic pricing helps the platform manage demand by incentivizing drivers to be available during high-demand periods and discouraging riders from requesting rides during peak times.
- Revenue Optimization: By adjusting prices based on supply and demand, the platform can maximize revenue and profitability.
- Improved Rider Experience: Dynamic pricing can help ensure that riders can consistently find available drivers, even during periods of high demand.
Challenges:
- Potential Rider Backlash: Sudden and significant price increases during peak times may be perceived as unfair by riders, leading to customer dissatisfaction and potential regulatory scrutiny.
- Driver Compensation Concerns: Drivers may feel that the platform is unfairly profiting from the dynamic pricing model, leading to potential conflicts and driver turnover.
- Complexity of Implementation: Effectively implementing a dynamic pricing model requires sophisticated algorithms and data analysis to accurately predict and respond to changes in supply and demand.
4. Advertising and Partnerships
Taxi app like Uber with feature that can generate additional revenue through advertising and strategic partnerships with complementary businesses.
Advertising Revenue:
- In-app Advertising: The platform can sell advertising space within the app, allowing businesses to reach a targeted audience of riders.
- Sponsored Content: The platform can offer sponsored content, such as featured promotions or branded experiences, to generate revenue.
Partnership Revenue:
- Affiliate Marketing: The platform can earn commissions by referring riders to partner businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, or other transportation services.
- Co-branded Offerings: The platform can collaborate with partners to create co-branded products or services, sharing the revenue generated.
Advantages:
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Advertising and partnerships can provide additional revenue sources, reducing the platform’s reliance on commission-based or subscription-based models.
- Leveraging Existing User Base: The platform can monetize its user base by offering targeted advertising and partnership opportunities to businesses.
- Enhancing User Experience: Riders can benefit from additional value and an improved user experience through carefully chosen partnerships and sponsored content.
Challenges:
- Balancing User Experience: Integrating advertising and partnerships into the app must be done in a way that does not disrupt the user experience or undermine the platform’s core value proposition.
- Maintaining Relevance: The platform must continuously identify and secure partnerships that are relevant and valuable to its user base, which can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Partnerships and advertising may be subject to a number of rules, including disclosure obligations and data protection laws, which need to be carefully considered.
5. Data Monetization
Uber-like apps collect a vast amount of data, including rider behavior, traffic patterns, and driver performance. This data can be monetized by the platform in various ways.
Data-driven Services:
- Predictive Analytics: The platform can leverage its data to provide predictive analytics services, such as demand forecasting and route optimization, to businesses or local governments.
- Targeted Advertising: The platform can use its data to offer highly targeted advertising opportunities to businesses, leveraging its insights into user preferences and behavior.
Data Licensing:
- Data Licensing to Third Parties: The platform can license its data to third-party organizations, such as research firms or urban planning agencies, for a fee.
- Data-as-a-Service (DaaS): The platform can offer a DaaS model, where it provides access to its data through an API or data platform, generating revenue from subscription fees or usage-based pricing.
Advantages:
- Monetizing Existing Assets: The platform can generate additional revenue by leveraging the valuable data it has already collected, without requiring significant additional investment.
- Competitive Advantage: The platform’s data-driven insights can provide a competitive edge, allowing it to offer unique services or optimize its own operations.
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Data monetization can serve as a complementary revenue source, reducing the platform’s reliance on commission-based or subscription-based models.
Challenges:
- Data Privacy and Regulations: The platform must ensure strict compliance with data privacy laws and regulations, which can be complex and evolving.
- Data Quality and Reliability: The platform must maintain high-quality, reliable data to ensure the accuracy and credibility of its data-driven services and offerings.
- Competitive Landscape: As the on-demand transportation industry matures, other platforms may also seek to monetize their data, increasing competition in this revenue stream.
6. Ancillary Services and Products
Uber-like apps can expand their revenue streams by offering ancillary services and products that complement their core transportation offerings.
Ancillary Services:
- Delivery Services: The platform can leverage its driver network to offer delivery services for food, groceries, or other goods.
- Financial Services: The platform can provide financial services, such as lending or insurance, to its drivers or riders.
Ancillary Products:
- Branded Merchandise: The platform can sell branded merchandise, such as apparel or accessories, to its users.
- In-app Purchases: The platform can offer in-app purchases, such as upgrades or premium features, to enhance the user experience.
Advantages:
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Ancillary services and products can provide additional revenue sources, reducing the platform’s reliance on its core transportation offerings.
- Increased Customer Engagement: Offering complementary services and products can help the platform deepen its relationship with users and increase customer loyalty.
- Leveraging Existing Infrastructure: The platform can leverage its existing driver network, technology, and user base to expand into ancillary offerings, potentially achieving economies of scale.
Challenges:
- Operational Complexity: Expanding into ancillary services and products can increase the platform’s operational complexity, requiring additional resources and expertise.
- Potential Dilution of Core Offering: The platform must ensure that its ancillary offerings do not detract from or dilute the quality of its core transportation services.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ancillary services, such as financial products, may be subject to additional regulatory requirements, which the platform must navigate.
Interested to develop a standout Taxi Booking App?
7xcel help you build a tailored taxi app using cutting-edge techs & advanced algorithms, enhancing user experience to its fullest potential.
Implementing Effective Monetization Strategies
Developing a successful revenue model for an Uber-like app requires a strategic and multifaceted approach. Here are some best practices to consider:
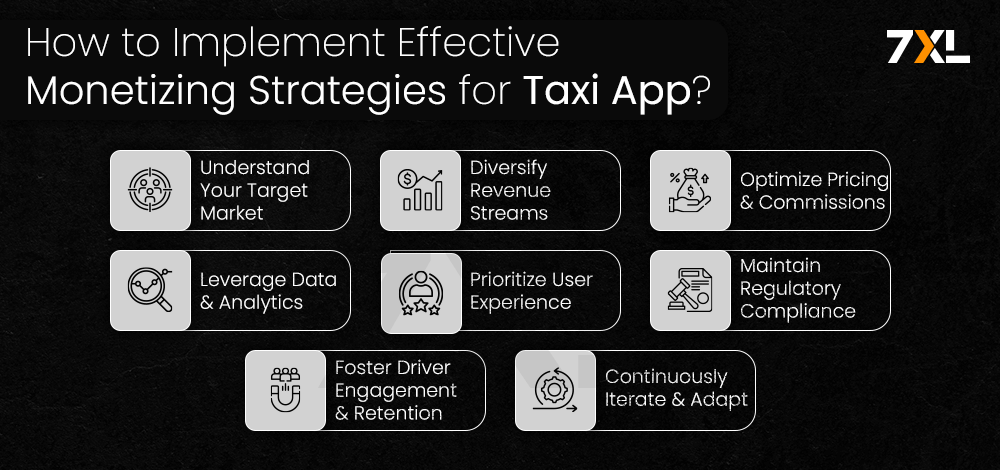
Understand Your Target Market:
Conduct thorough market research to understand the needs, preferences, and pain points of your target riders and drivers. This will help you tailor your monetization strategies to their specific requirements.
Diversify Revenue Streams
Implement a mix of revenue models, such as commission-based, subscription-based, and ancillary services, to create a balanced and resilient revenue structure. This will help you mitigate the risks associated with relying on a single revenue source.
Optimize Pricing and Commissions:
Carefully analyze your costs, market conditions, and user behavior to set competitive and sustainable pricing and commission structures. Regularly review and adjust these parameters to maintain profitability and user satisfaction.
Leverage Data and Analytics
Utilize the wealth of data collected by your Uber-like app to generate valuable insights that can inform your monetization strategies. This may include predictive analytics, targeted advertising, and data licensing opportunities.
Prioritize User Experience
Ensure that your monetization strategies enhance, rather than detract from, the user experience. Seamless integration of revenue-generating features and transparent pricing can help build trust and loyalty among your riders and drivers.
Maintain Regulatory Compliance
Stay up-to-date with the evolving regulatory landscape and ensure that your monetization practices adhere to all relevant laws and regulations, particularly in areas such as data privacy, labour laws, and consumer protection.
Foster Driver Engagement and Retention
Develop monetization strategies that align the interests of your platform, riders, and drivers. Ensure fair compensation and incentives for your driver network to maintain a reliable and satisfied workforce.
Continuously Iterate and Adapt
Monitor the performance of your monetization strategies, gather feedback from users, and be prepared to adapt and pivot as market conditions and user preferences evolve.
By implementing these best practices and leveraging the diverse revenue models discussed in this blog, you can unlock the full potential of your Uber-like app and establish a sustainable and profitable business in the dynamic on-demand transportation industry.
Conclusion
The on-demand transportation industry, inspired by Uber, offers significant opportunities for entrepreneurs to develop similar apps. Success in this space requires both a user-friendly platform and effective monetization strategies. Key revenue models include commission-based systems, subscriptions, dynamic pricing, advertising, partnerships, data monetization, and ancillary services. Combining these strategies can create a balanced and sustainable revenue structure. By understanding the industry, using data insights, and prioritizing user experience, entrepreneurs can build successful and growth-oriented Uber-like apps.








