Quick Summary:
Doctor-on-demand applications revolutionize healthcare by offering convenient access to medical services. However, protecting sensitive data is crucial. This blog explores the criticality of data protection in healthcare apps, potential risks of data breaches, types of sensitive data, best practices for data protection, regulatory requirements, and the role of IT service providers.
In this blog, we’re going to discuss📝
- Why Is Data Protection Critical in Healthcare Apps?
- What Are the Potential Risks of Data Breaches in Doctor-on-Demand Applications?
- Common Types of Sensitive Data in Doctor-on-Demand Applications
- Building a Secure Doctor-on-Demand App: Key Features and Functionalities
- Best Practices for Data Protection
- Regulatory Requirements and Compliance Standards
- Role of IT Service Providers in Data Protection
With the rapid rise of Telehealth services, doctor-on-demand applications have become an essential part of modern healthcare. With the unmatched ease of these applications, patients can receive medical care while lounging in their own homes.
However, this convenience comes with significant responsibilities, particularly regarding the protection of sensitive data. In this blog , we will delve into why data protection is critical in healthcare apps, the potential risks of data breaches, common types of sensitive data, best practices for data protection, regulatory requirements, and how IT service providers can assist in safeguarding this data.
Why Is Data Protection Critical in Healthcare Apps?
Data protection in healthcare apps is of utmost importance for several reasons:
Patient Trust:
Patients trust healthcare providers with their most sensitive information. Protecting this data is essential to maintaining this trust. A data breach can significantly damage the reputation of the healthcare provider and lead to loss of patient confidence.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Healthcare providers are legally required to protect patient data. High fines and possible legal repercussions might arise from breaking laws like GDPR and HIPAA. Ensuring data protection helps avoid legal repercussions and maintain compliance.
Financial Impact:
Data breaches can be financially devastating. As per the report, the average cost of a data breach in the healthcare industry is $7.13 million, the highest among all industries. Protecting data helps avoid these substantial financial losses.
Patient Safety:
Inaccurate or compromised data can lead to medical errors, jeopardizing patient safety. Safe and efficient healthcare depends on maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of medical records.
What Are the Potential Risks of Data Breaches in Doctor-on-Demand Applications?
Doctor-on-demand applications are prime targets for cyber attacks due to the sensitive nature of the data they handle. The potential risks of data breaches include:
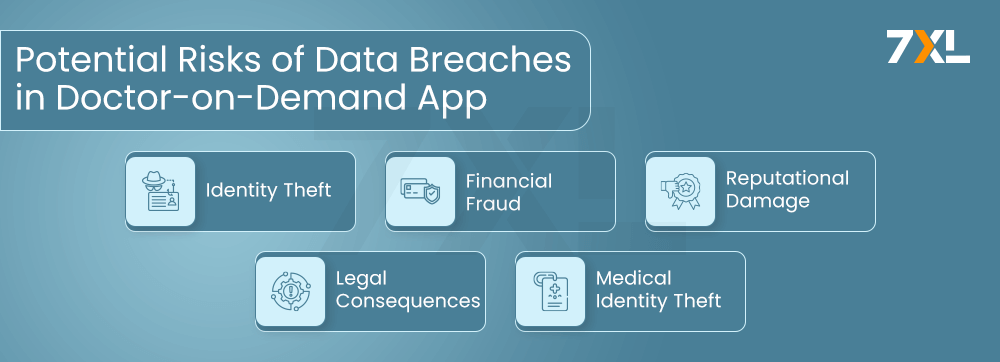
- Identity Theft: Personal Identification Information (PII) such as names, addresses, & social security numbers can be stolen and used for identity theft. In 2020, identity theft affected 1 in 20 Americans, highlighting the need for stringent data protection measures.
- Financial Fraud: Payment and insurance information can be exploited for financial fraud. The healthcare sector saw a 42% increase in payment fraud attempts in 2021, emphasizing the importance of protecting financial data.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach can severely damage the reputation of the healthcare provider, leading to loss of patient trust and potential business losses.
- Legal Consequences: Breaches can result in non-compliance with regulatory requirements, leading to hefty fines and legal actions. GDPR violations can result in fines of up to 4% of global annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher.
- Medical Identity Theft: Unauthorized access to medical records can lead to medical identity theft, where someone receives medical treatment under another person’s identity. This can result in incorrect medical records and potential harm to the patient.
Common Types of Sensitive Data in Doctor-on-Demand Applications
Doctor-on-demand applications handle a variety of sensitive information that must be meticulously protected:
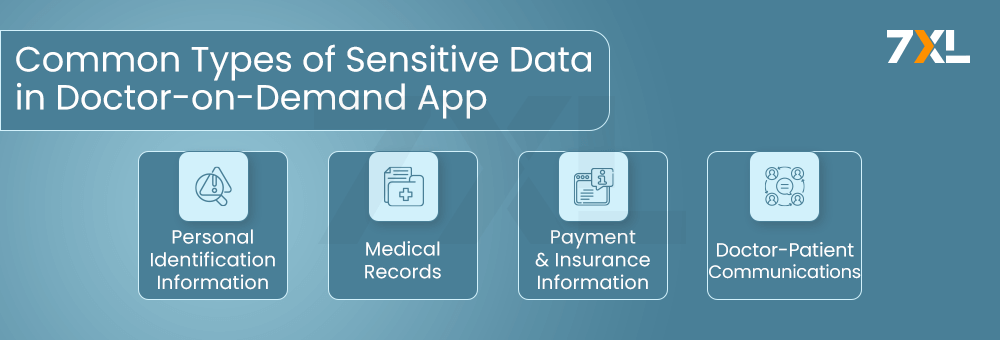
Personal Identification Information (PII):
This includes patients’ names, addresses, contact details, and social security numbers. PII is crucial for patient identification, appointment scheduling, and billing purposes.
Medical Records:
These records comprise detailed health histories, diagnoses, treatment plans, lab results, and imaging reports. Medical records are essential for providing accurate and personalized care. However, they are also highly valued on the black market, with health records fetching up to $250 per record compared to $5 for a credit card number.
Payment and Insurance Information:
This data includes billing details, credit card information, and insurance coverage specifics. It is critical for processing payments and managing insurance claims.
Doctor-Patient Communications:
Messages, prescriptions, and diagnostic reports shared between doctors and patients often contain sensitive medical information.
Building a Secure Doctor-on-Demand App: Key Features and Functionalities
To create a successful and secure doctor-on-demand app, you need to incorporate the following key features and functionalities:
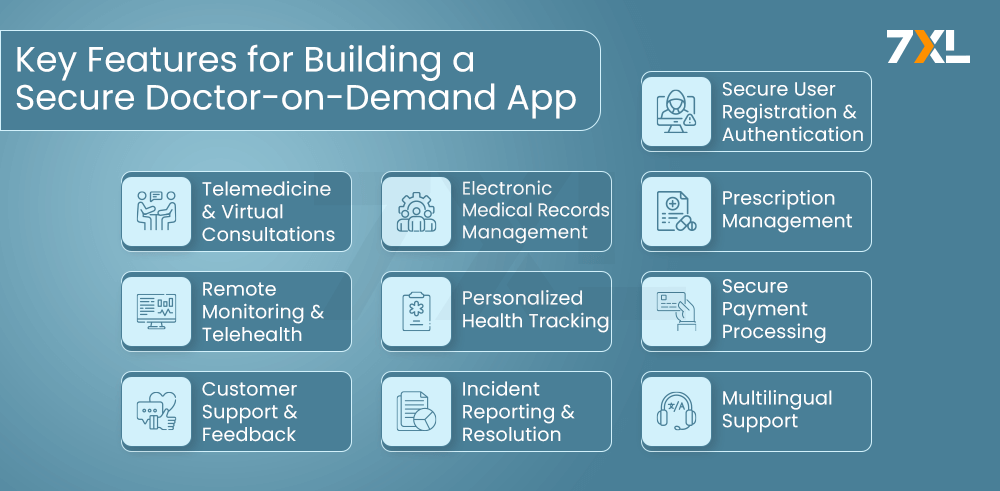
Secure User Registration and Authentication:
Implement a secure user registration and authentication process, including options for multi-factor authentication and biometric verification, to protect patient accounts from unauthorized access.
Telemedicine and Virtual Consultations:
Provide a seamless and HIPAA-compliant platform for patients to conduct video consultations with healthcare providers, ensuring the confidentiality of their interactions.
Electronic Medical Records Management:
Enable patients to securely access, manage, and share their medical records, including test results, prescriptions, and past consultations, with authorized healthcare providers.
Prescription Management:
Offer a secure and convenient platform for patients to manage their prescriptions, including refill requests, medication reminders, and secure storage of prescription information.
Remote Monitoring and Telehealth:
Integrate remote monitoring capabilities, such as the ability to share medical data and vital signs, to facilitate ongoing care and disease management, while ensuring the privacy and security of patient-generated health data.
Personalized Health Tracking:
Leverage data analytics and AI to provide personalized health recommendations, wellness programs, and disease management tools to empower patients and improve their overall well-being, while adhering to strict data privacy and security protocols.
Secure Payment Processing:
Integrate with HIPAA-compliant payment gateways to handle financial transactions securely, offering patients a range of payment options and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations.
Customer Support and Feedback:
Provide patients with a dedicated customer support channel, allowing them to report issues, request changes, or provide feedback, and guarantee that their issues are handled efficiently and quickly while protecting the privacy of any shared sensitive information.
Incident Reporting and Resolution:
Implement a comprehensive incident reporting and resolution system, enabling patients and healthcare providers to report security incidents or privacy concerns, and ensuring that appropriate actions are taken to address them in a timely & effective manner.
Multilingual Support:
Cater to a diverse patient population by providing multilingual support, ensuring accessibility and inclusivity, while preserving patient data’s confidentiality and security across many languages
Best Practices for Data Protection
To safeguard sensitive data in doctor-on-demand applications, implementing robust security measures are essential:
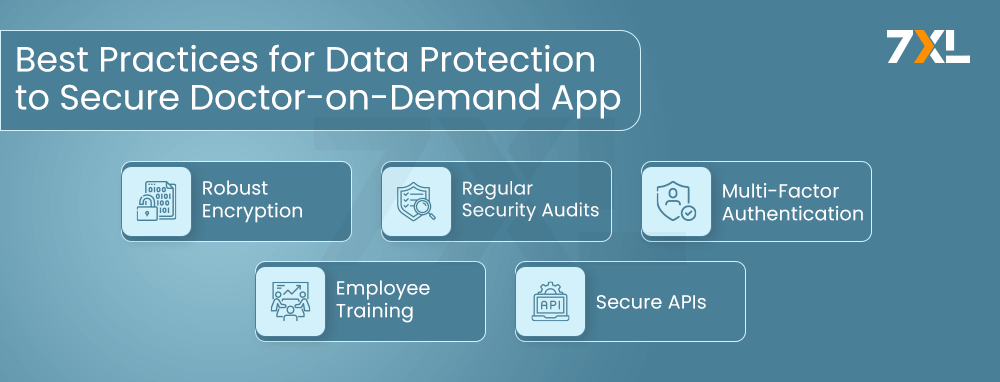
Robust Encryption:
To stop illegal access, use sophisticated encryption techniques for data that is in transit and at rest. Encryption standards such as AES-256 and TLS 1.2+ for data transmission provide strong protection. End-to-end encryption ensures that data remains confidential from the point of origin to its destination.
Regular Security Audits:
To find & fix possible security flaws, conduct regular audits and vulnerability analyses. Frequent audits contribute to the maintenance of current and efficient security protocols. Penetration testing by outside security specialists can reveal flaws that are not immediately apparent.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Enhance login security by requiring multiple forms of verification. Even in the unlikely event that login credentials are hacked, MFA lowers the risk of unwanted access. Implementing MFA for all user accounts, including patients, healthcare providers, and administrative staff, adds an extra layer of security.
Employee Training:
Educate staff about data security practices and phishing prevention. Regular training helps employees recognize and respond to potential security threats. Employees should be trained on the latest cyber security threats, safe handling of sensitive data, and incident reporting procedures.
Secure APIs:
Ensure secure API integration and keep software updated with the latest security patches. Securing APIs prevents attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in the application’s interface. Implementing API security best practices, such as rate limiting, input validation, and OAuth 2.0 for authentication, can help protect against API-related threats.
Planning to Develop an On-Demand Doctor App?
Build your cutting-edge doctor app with 7xcel – quicker, simpler, features-packed to enhance patient care.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance Standards
Compliance with regulatory standards is crucial for protecting sensitive data and avoiding legal penalties. Key regulations include:
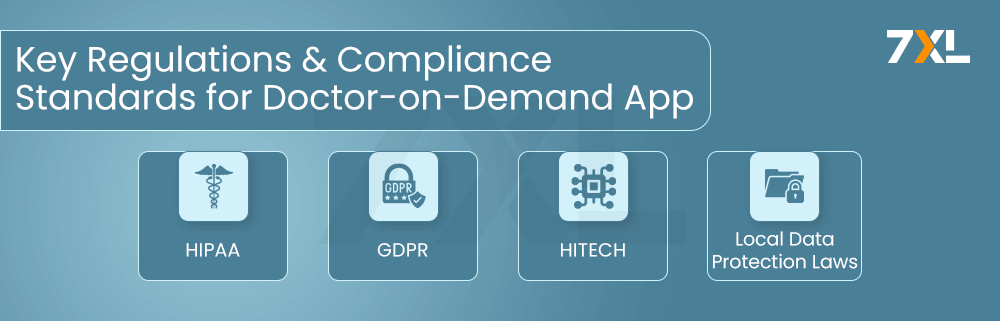
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
U.S. laws that set standards for protecting health information. To safeguard electronic health records, administrative, technical, and physical security measures must be implemented in accordance with HIPAA. Covered businesses need to ensure data encryption, implement access controls, & conduct regular risk assessments in order to comply with HIPAA standards. Noncompliance may result in severe fines and legal repercussions.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
EU regulation that governs data protection and privacy. GDPR puts stringent rules on data processing and is applicable to any business that handles the data of people of the EU. In order to process personal data, organizations must get individuals’ express consent, be open and honest about how they use it, and protect their right to have their data erased and transferred. Fines for violating the GDPR may reach up to 4% of international revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH):
U.S. law promoting the adoption of health IT with stringent data protection requirements. HITECH strengthens HIPAA regulations and introduces additional security measures. It incentivizes healthcare providers to adopt electronic health records (EHR) and implement comprehensive data protection strategies. HITECH also includes breach notification requirements, ensuring that affected individuals are promptly informed of data breaches.
Local Data Protection Laws:
Compliance with relevant local and international data protection laws. Different regions have specific regulations that organizations must follow to ensure data protection. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants California residents enhanced privacy rights and control over their personal information. Organizations must stay informed about evolving data protection laws and implement measures to comply with applicable regulations.
Role of IT Service Providers in Data Protection
IT service providers play a pivotal role in ensuring data protection for doctor-on-demand applications. Partnering with a specialized Doctor-On-Demand App Development Company can help implement robust security measures tailored to the unique needs of healthcare platforms.
These companies offer advanced encryption, secure data storage solutions, and compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and HITECH, ensuring that sensitive patient information is fully protected. They also provide regular security updates and monitoring to safeguard the app against potential threats.
Managed Security Services:
Continuous monitoring and management of security systems to prevent breaches. Managed services provide proactive security measures and incident response capabilities. IT service providers utilize advanced security tools and techniques, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, to detect & respond to threats in real-time. By outsourcing security management to experts, healthcare providers can focus on delivering quality care.
Compliance Assessments:
Regular evaluations to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements. Compliance assessments help organizations identify gaps and implement necessary improvements. IT service providers conduct comprehensive assessments to evaluate an organization’s security posture, identify non-compliance issues, and recommend corrective actions. Regular compliance assessments ensure that healthcare providers meet regulatory standards and avoid legal penalties.
Advanced Security Solutions:
Implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures. Advanced solutions provide multiple layers of protection against various threats. IT service providers deploy next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and endpoint security solutions to safeguard sensitive data. These technologies help detect and block malicious activities, providing robust protection for doctor-on-demand applications.
Incident Response:
Rapid response to security incidents to minimize damage. Incident response teams are trained to handle security breaches efficiently and effectively. IT service providers develop and implement incident response plans tailored to healthcare organizations’ specific needs. These plans include procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security incidents. Prompt and effective incident response minimizes the impact of breaches and ensures business continuity.
Secure Cloud Solutions:
Safe and compliant storage and backup solutions. Secure cloud services ensure that data is protected and can be restored in case of an incident. IT service providers offer cloud-based data storage and backup solutions that comply with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR. These solutions provide scalable and cost-effective data storage options while ensuring data availability, integrity, and confidentiality. Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions enable quick data restoration in the event of a breach or system failure.
Conclusion
Protecting sensitive information in doctor-on-demand apps is essential for maintaining patient trust and ensuring the success of Telehealth services. This requires implementing robust security measures, adhering to regulatory standards, and leveraging the expertise of IT professionals.
Healthcare providers must prioritize data security by staying updated on emerging risks, regularly updating security processes, and fostering a culture of security awareness. By doing so, they not only comply with legal requirements but also uphold ethical standards, ultimately enhancing patient confidence and supporting the long-term viability of Telehealth services.