Quick Summary:
Educational apps like Coursera generate revenue through various strategies, including course fees, subscription models, and selling verified certificates. They also partner with educational institutions, offer corporate training solutions, and monetize user data. Additional income streams come from in-app purchases, sponsored content, and career services, ensuring diverse and sustainable revenue sources in the competitive online education market.
In this blog, we’re going to discuss📝
Educational apps like Coursera have revolutionized access to learning by offering courses from top institutions worldwide. Their success, however, depends not just on educational content but also on sustainable revenue generation. Coursera and similar platforms monetize through course fees, subscriptions, partnerships, and corporate training solutions.
By diversifying their revenue streams, they ensure financial viability while continuing to expand and enhance their educational offerings. This introduction will explore the various monetization strategies that sustain these platforms in a competitive market.
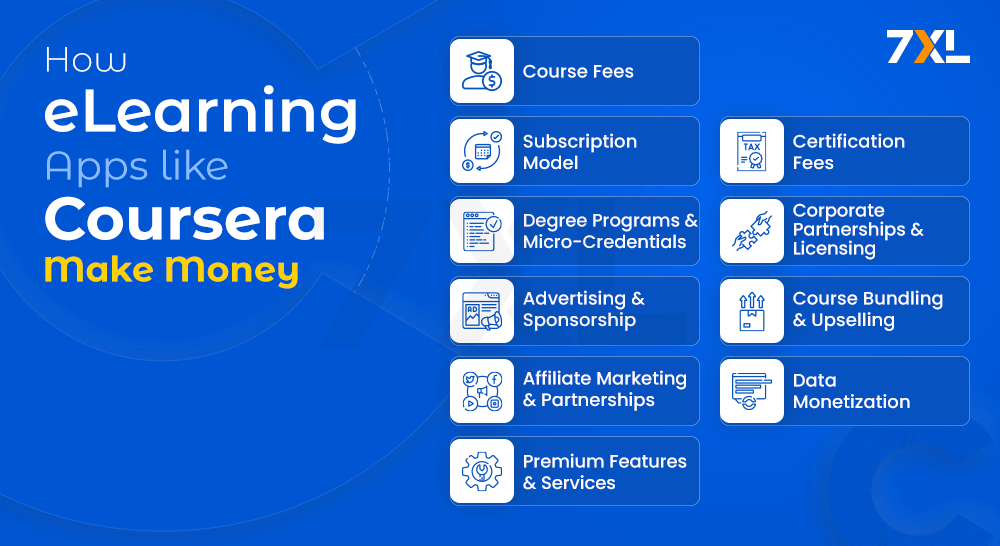
1. Course Fees
Charging fees for individual courses is a primary revenue stream for educational apps. This model allows users to pay for access to specific courses they are interested in, providing flexibility and choice.
How It Works:
- One-Time Payment: Users make a one-time payment to access a course, which grants them access to all texts, assignments, and video lectures for the course.
- Tiered Pricing: Courses are priced based on factors such as the content’s depth, the instructor’s credentials, course length, and the institution offering the course. More comprehensive or specialized courses tend to have higher fees.
Advantages:
- Direct Revenue: Provides immediate income from course sales, which can be significant given the vast number of users and courses offered.
- User Flexibility: Allows users to choose and pay for courses they are specifically interested in, rather than committing to a broader subscription.
Disadvantages:
- High Competition: Users may be reluctant to pay for courses if there are free alternatives available.
- Variable Income: Revenue can fluctuate based on course popularity and enrollment numbers.
Example:
- Coursera: Charges fees for individual courses, which can range from $29 to $99 per course, depending on the content and provider. Some specialized courses or certifications may be priced higher.
2. Subscription Model
Users of the subscription model get unrestricted access to a wide range of courses and resources for a recurring fee. This model is effective in creating a steady and predictable revenue stream while encouraging continuous engagement.
How It Works:
- Monthly/Annual Plans: Users subscribe to a plan that allows them to access a vast library of courses for a set period, typically monthly or annually.
- Tiered Access: Different subscription tiers offer varying levels of access and benefits. For example, a basic subscription may provide access to a standard selection of courses, while a premium subscription might include additional features like advanced courses, project-based learning, or mentorship.
Advantages:
- Predictable Income: Generates consistent revenue through regular subscription payments, aiding in financial planning and stability.
- Increased Engagement: Encourages users to explore a wider range of courses and resources, enhancing platform usage and retention.
Disadvantages:
- Retention Challenge: Retaining subscribers over time can be challenging, especially if users feel they have exhausted the available content.
- Upfront Commitment: Some users may be hesitant to commit to a subscription without first sampling the platform’s offerings.
Example:
- Coursera Plus: offers a membership service for an annual charge, usually around $399, that grants unrestricted access to over 3,000 courses, professional credentials, and specialties.
3. Certification Fees
Charging fees for certificates upon course completion is a prevalent monetization strategy. Certifications provide added value by validating the skills and knowledge gained, which can enhance the user’s resume and career prospects.
How It Works:
- Paid Certificates: Users can pay a fee to obtain a certificate of completion after finishing a course. This certificate typically includes the user’s name, course details, and the institution’s logo.
- Credential Value: Certificates from recognized institutions or industry leaders carry significant value and can be a key motivator for users to complete courses.
Advantages:
- High Value: Certificates offer tangible benefits, justifying the cost for many users, particularly those looking to advance their careers.
- Revenue Boost: Provides an additional revenue stream beyond the initial course fees.
Disadvantages:
- Extra Cost: The additional fee for a certificate might deter some users who are only interested in the course content.
- Perceived Value: The value of certificates can vary depending on the institution or course provider, affecting users’ willingness to pay.
Examples:
- Coursera: Charges for verified certificates, which typically range from $40 to $100 per course, depending on the course and institution.
4. Degree Programs and Micro-Credentials
Offering online degree programs and micro-credentials is a significant revenue generator. These programs are often more comprehensive and expensive than individual courses, appealing to learners seeking formal education and professional development.
How It Works:
- Degree Programs: Users can enroll in fully online degree programs, leading to undergraduate or graduate qualifications. These programs are designed in collaboration with universities and can be completed entirely through the platform.
- Micro-Credentials: These are shorter, focused programs that provide specialized skills and knowledge in a particular area. They are often stackable, meaning credits earned can be applied towards a degree program.
Advantages:
- High Revenue Potential: Degree programs and micro-credentials have higher price points, leading to substantial revenue.
- Comprehensive Education: Offers a more in-depth educational experience that can attract a broader audience, including working professionals seeking to advance their careers.
Disadvantages:
- High Costs: Developing and maintaining degree programs requires significant investment in content creation and partnerships with educational institutions.
- Longer Sales Cycle: Convincing users to enroll in degree programs can take longer and involve more decision-making compared to individual courses.
Examples:
- Coursera: Collaborates with universities to offer online courses in fields like business, computer science, and public health. These programs can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $50,000, depending on the degree and institution.
Planning to Develop an eLearning App like Coursera?
Build your Coursera-competing eLearning app with 7xcel- faster, easier, & with the features that keep learners engaged.
5. Corporate Partnerships and Licensing
Educational apps can generate significant revenue by partnering with corporations to provide training and development programs for employees. This B2B approach leverages the app’s content to meet corporate training needs, creating a substantial income source through bulk licensing agreements.
How It Works:
- Corporate Training Programs: The platform offers tailored courses and learning paths designed for corporate clients to enhance their employees’ skills and knowledge.
- Bulk Licensing: Companies purchase licenses for multiple employees, providing them access to the app’s course catalog and resources. These agreements can be structured as annual contracts, generating steady revenue.
Advantages:
- Stable Revenue: Corporate partnerships provide a steady income stream through long-term contracts, offering financial stability.
- Market Expansion: Expands the platform’s reach into the corporate training sector, tapping into a lucrative market for professional development.
Disadvantages:
- Customization Required: Tailoring content and managing relationships with corporate clients can be resource-intensive.
- Competition: The corporate training market is competitive, requiring differentiation through content quality and service.
Examples:
- Coursera for Business: Offers corporate training solutions that allow companies to provide their employees with access to a large group of courses and specializations, supporting workforce development.
6. Advertising and Sponsorship
In-app advertising and sponsorship deals are additional revenue streams for educational apps. These platforms can attract advertisers interested in targeting a specific demographic or promoting educational content, leveraging the app’s user base for marketing opportunities.
How It Works:
- In-App Ads: Display advertisements within the app, including banners, video ads, and sponsored content. These ads can be targeted based on user demographics and interests.
- Sponsorship Deals: Partner with companies to sponsor specific courses, programs, or events, providing them with visibility and branding opportunities.
Advantages:
- Additional Revenue: Generates income without directly charging users for access, enhancing profitability.
- Brand Partnerships: Offers opportunities for collaborations with educational and industry brands, creating mutually beneficial relationships.
Disadvantages:
- User Experience: Excessive or intrusive ads can disrupt the user experience, leading to dissatisfaction and potential user churn.
- Privacy Concerns: Targeted advertising must comply with privacy regulations to avoid user data misuse.
Examples:
- Coursera: Partners with organizations for sponsored courses or events, providing a platform for brands to reach a targeted audience interested in education and professional development.
7. Course Bundling and Upselling
Bundling courses together and upselling related courses or services is an effective way to increase the average revenue per user. Collaborating with an experienced eLearning App Development Company can help in designing and implementing these strategies seamlessly.
Their expertise ensures that the platform is optimized for offering bundled courses, personalized recommendations, and targeted upselling, which enhances the overall value and learning experience for users while driving revenue growth.
How It Works:
- Course Bundles: The platform offers discounts on packages of related courses, incentivizing users to buy multiple courses at once.
- Upselling: Users are recommended additional courses, certifications, or premium services that complement their current course selections or career goals.
Advantages:
- Increased Sales: Encourages users to spend more by offering discounts on bundled content, increasing overall revenue.
- Enhanced Learning: Provides users with a comprehensive learning path, improving satisfaction and retention.
Disadvantages:
- Discount Dependency: Users may become accustomed to discounts and expect reduced prices on future purchases.
- Complexity: Managing and promoting bundles effectively requires careful planning and marketing.
Examples:
- Coursera: Offers specializations that combine multiple courses at a reduced price, providing a structured learning experience that covers a broader skill set or topic area.
8. Affiliate Marketing and Partnerships
Educational apps can earn revenue through affiliate marketing and partnerships with other educational platforms or services. By promoting partner content, these apps can earn commissions on referrals and expand their course offerings without additional content creation.
How It Works:
- Affiliate Links: The app promotes courses or services from partner platforms, earning a commission on sales generated through referral links.
- Cross-Promotions: Collaborate with other educational providers to offer joint courses or programs, sharing revenue from enrollments and course sales.
Advantages:
- Revenue Sharing: Provides an additional income stream without the need to develop new content, leveraging the partner’s offerings.
- Extended Offerings: Expands the platform’s course catalog by including partner content, offering users more choices and enhancing the app’s value proposition.
Disadvantages:
- Quality Control: Ensuring that partner content meets the platform’s quality standards is essential to maintain user trust and satisfaction.
- Revenue Split: The revenue is shared with partners, potentially reducing the overall profitability.
Examples:
- Coursera: May partner with other educational providers to offer joint programs and courses, earning commissions on referrals and expanding the course offerings available to users.
9. Data Monetization
Data monetization involves analyzing and selling anonymized user data to third parties, such as educational institutions and research organizations. This model leverages valuable insights gained from user interactions with the app to generate revenue.
How It Works:
- Data Analysis: The platform collects and analyzes data on user behavior, course completion rates, learning preferences, and more.
- Data Sales: Aggregated and anonymized data is sold to third parties for market research, educational insights, and strategic planning.
Advantages:
- High Value: User data provides valuable insights for improving educational content, marketing strategies, and product development.
- Non-Disruptive: Generates revenue without directly impacting the user experience, making it an attractive option for additional income.
Disadvantages:
- Privacy Concerns: Requires strict adherence to privacy regulations and ethical guidelines to avoid legal and reputational issues.
- User Trust: Maintaining user trust is critical, as data monetization practices can raise concerns about data privacy and security.
Examples:
- Coursera: Could sell anonymized data to educational institutions and companies to help them understand trends in online learning and optimize their educational offerings.
10. Premium Features and Services
Offering premium features and services, such as advanced analytics, personalized learning paths, or exclusive content, provides a way to further monetize the platform. Users can access these premium offerings for an additional fee, enhancing their overall learning experience.
How It Works:
- Premium Content: Charge users for access to exclusive courses, advanced certifications, or specialized learning materials that are not available in the standard offerings.
- Advanced Features: Offer premium services such as detailed progress analytics, personalized tutoring, one-on-one coaching, or access to professional networks.
Advantages:
- Increased Revenue: Provides an additional income stream from users willing to pay for enhanced learning experiences and advanced features.
- User Value: Adds significant value to the user experience, promoting higher engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
Disadvantages:
- Exclusive Cost: High fees for premium features may deter some users who are unable or unwilling to pay for additional services.
- Differentiation Required: The platform must clearly demonstrate the added value of premium features to justify the cost to users.
Examples:
- Coursera: Offers premium features like graded assignments, capstone projects, and personalized course recommendations, which can be accessed for a fee, providing users with a richer learning experience.
Conclusion
Educational apps like Coursera employ a variety of monetization strategies to generate revenue and sustain their operations. By utilizing models such as course fees, subscriptions, certification fees, degree programs, corporate partnerships, advertising, data monetization, and premium services, these platforms create diverse revenue streams while delivering significant value to users.
Choosing the right combination of these strategies will depend on the app’s target audience, market conditions, and competitive landscape, leading to a sustainable and profitable business model in the online education industry.








